
A marine steam turbine manufactured by MAN Energy Solutionsĭevelopment in liquefied natural gas (LNG) fueled engines are gaining recognition for their low emissions and cost advantages.

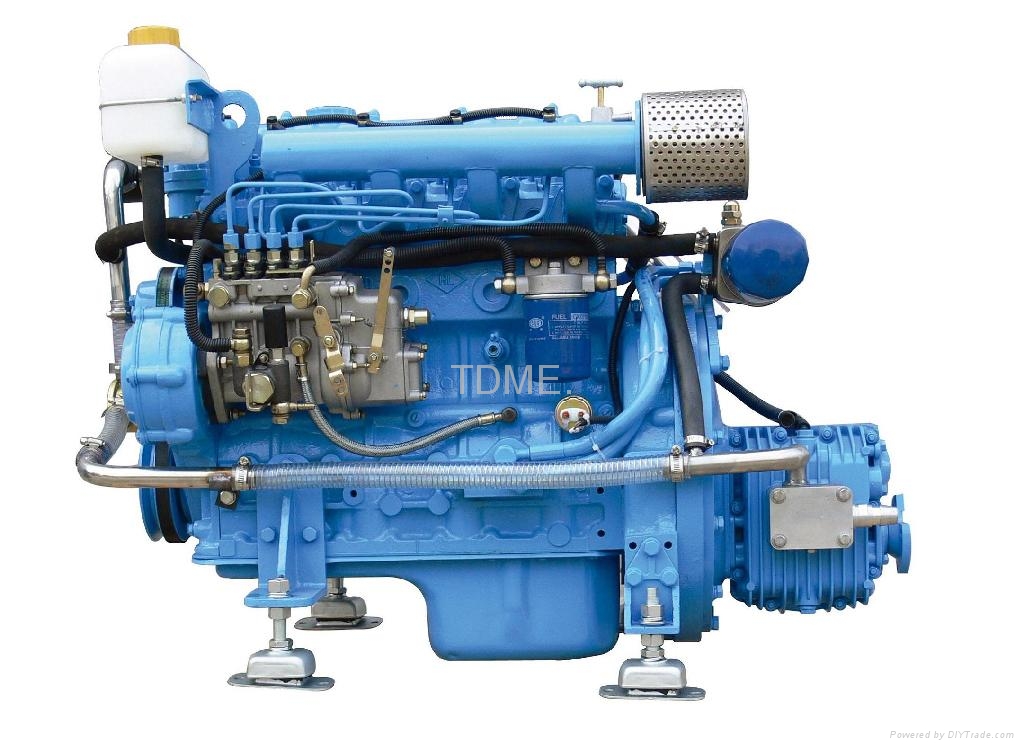
Electric motors using battery packs have been used for propulsion on submarines and electric boats and have been proposed for energy-efficient propulsion. Marine nuclear reactors, which appeared in the 1950s, produce steam to propel warships and icebreakers commercial application, attempted late that decade, failed to catch on. During the 20th century it was replaced by two-stroke or four-stroke diesel engines, outboard motors, and gas turbine engines on faster ships. The first advanced mechanical means of marine propulsion was the marine steam engine, introduced in the early 19th century. Rowed galleys, some equipped with sail, played an important early role in early human seafaring and warfares. Human-powered paddles and oars, and later, sails were the first forms of marine propulsion. Marine engineering is the discipline concerned with the engineering design process of marine propulsion systems. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of an electric motor or internal combustion engine driving a propeller, or less frequently, in pump-jets, an impeller. Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a watercraft through water. Rolls-Royce Marine Spey, a gas turbine developed by Rolls-Royce Holdings in the 1960s for marine propulsion. JSTOR ( December 2009) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message).Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.įind sources: "Marine propulsion" – news Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. This article needs additional citations for verification.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
